Understanding the Long-Term Risks of Intermittent Fasting: A Balanced Perspective
Intermittent fasting (IF), characterized by cycles of eating and fasting, has gained popularity for its potential benefits in weight management and metabolic health. However, emerging research highlights significant long-term risks that warrant careful consideration. Below, we explore these risks, contextualize them alongside short-term benefits, and provide actionable guidance for those considering IF.
Key Long-Term Risks
-
Cardiovascular Health Concerns Recent studies raise alarms about the cardiovascular implications of prolonged IF. A 2024 analysis of over 20,000 adults found that individuals practicing an 8-hour time-restricted eating window had a 91% higher risk of cardiovascular death compared to those eating over 12–16 hours daily. This risk was particularly pronounced in individuals with pre-existing heart disease or cancer. While short-term trials suggest IF may improve blood pressure and cholesterol, the long-term data indicate potential harm, possibly due to metabolic stress or nutrient imbalances during extended fasting periods.
-
Metabolic and Hormonal Disruptions IF’s impact on metabolism remains double-edged. Although it enhances insulin sensitivity and lipid oxidation initially, prolonged fasting may lead to impaired glucose regulation and hypoglycemia, especially in individuals with diabetes or metabolic disorders. Hormonal imbalances, such as elevated cortisol (a stress hormone) and disruptions in thyroid function, have also been observed in long-term practitioners, potentially undermining metabolic health.
-
Nutritional Deficiencies and Muscle Loss Restricting eating windows often reduces opportunities to consume adequate nutrients. Over time, this can result in deficiencies in essential vitamins (e.g., B12, D), minerals (e.g., iron, magnesium), and protein, particularly if dietary choices are not carefully planned. Older adults face additional risks: IF may accelerate sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss) due to insufficient protein intake and prolonged catabolic states during fasting.
-
Psychological and Behavioral Impacts IF’s restrictive nature can exacerbate disordered eating patterns, such as binge eating or orthorexia, particularly in individuals predisposed to these behaviors. Mood disturbances, including irritability and anxiety, are commonly reported during fasting periods, and long-term adherence may strain social relationships centered around meals.
-
Gut Microbiome and Circadian Rhythm Interference The gut microbiome thrives on consistent nutrient intake. Extended fasting periods may disrupt microbial diversity, impairing digestion and immune function. Additionally, misaligning eating windows with the body’s circadian rhythm (e.g., skipping breakfast) can disturb sleep patterns and metabolic processes, compounding long-term health risks.
Contextualizing Short-Term Benefits IF’s appeal lies in its short-term advantages, including weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and reduced inflammation. For example, a 2021 review noted that IF can lower oxidative stress markers and enhance autophagy (cellular repair). However, these benefits often plateau after 6–12 months, and sustainability remains a challenge due to the risks outlined above.
Practical Advice for Safer Implementation Consult a Healthcare Provider: Before starting IF, discuss your medical history, especially if you have cardiovascular conditions, diabetes, or a history of eating disorders.
Prioritize Nutrient Density: Opt for whole foods rich in protein, fiber, and micronutrients during eating windows to mitigate deficiencies.
Avoid Extreme Protocols: Steer clear of fasting windows exceeding 12 hours, as these correlate with higher risks. The 12:12 method (12-hour fast) is a safer entry point.
Monitor Biomarkers: Regularly check blood pressure, cholesterol, and glucose levels to catch adverse effects early.
Adapt for Age and Activity: Older adults and athletes should ensure adequate protein intake and avoid fasting on high-activity days to preserve muscle mass.
Conclusion Intermittent fasting offers short-term metabolic benefits but carries significant long-term risks, particularly for cardiovascular health, hormonal balance, and mental well-being. Current evidence suggests that IF is not a one-size-fits-all solution and requires careful, individualized implementation. Those considering IF should weigh these risks against potential benefits and adopt strategies to minimize harm.
Takeaway: While IF can be a useful tool for some, its long-term safety profile remains uncertain. Prioritize balanced nutrition, regular health monitoring, and professional guidance to navigate this dietary approach safely.
Have questions or personal experiences with intermittent fasting? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
Also take time to read this article on Anabolic fasting .Anabolic fasting,combines intermittent fasting with targeted nutritional strategies to promote muscle gain and fat loss simultaneously. It involves cycling between fasting periods, typically 16/8 hours, and specific eating windows focused on high-protein, low-carb, and high-fat foods. This approach leverages research to boost metabolism, preserve muscle, and accelerate fat burning, making it effective for body transformation and long-term health

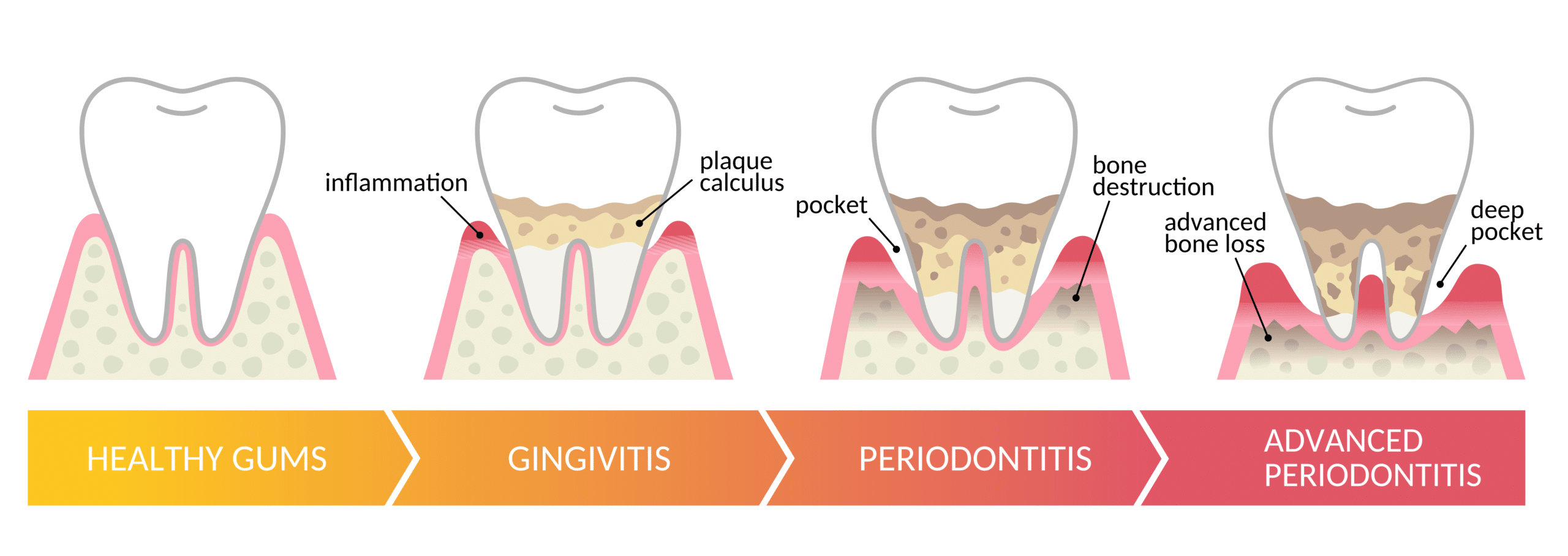
Pregnancy Gingivitis: A Comprehensive Guide for Expectant Mothers
Pregnancy gingivitis is a common oral health condition affecting the majority of expectant mothers, with prevalence rates ranging from 60-75%. This inflammatory gum condition is primarily triggered by hormonal changes during pregnancy that increase susceptibility to bacterial plaque. Research indicates that untreated gingivitis during pregnancy may be associated with adverse birth outcomes, including preterm birth and lower birth weight. However, the condition is both preventable and treatable with proper oral hygiene practices and professional dental care, which are considered safe throughout pregnancy. Current evidence emphasizes the importance of maintaining optimal oral health during pregnancy through regular dental visits, proper brushing and flossing techniques, and professional interventions when necessary.
Prevalence and Development of Pregnancy Gingivitis
Pregnancy gingivitis is remarkably common among expectant mothers, with studies consistently showing high prevalence rates across different populations. Between 60% and 70% of women experience pregnancy gingivitis, making it one of the most frequently encountered oral health issues during pregnancy. In some populations, the rates can be even higher, with research conducted in Nepal reporting a prevalence of 76.3% in the second trimester of pregnancy. Other studies have found varying rates, from 38% to as high as 93.75%, depending on the research methodology and population studied.
The condition typically follows a predictable timeline throughout pregnancy. Pregnancy gingivitis often first develops late in the first trimester, as hormonal changes begin to affect gum tissue responsiveness. The severity tends to increase as pregnancy progresses, usually peaking during the second trimester or around the eighth month of gestation. Importantly, the condition is generally temporary, with symptoms typically subsiding shortly after delivery as hormone levels return to pre-pregnancy states.
Research indicates that pregnant women are significantly more likely to develop gingivitis compared to non-pregnant women. One comparative study found that pregnant women were 1.94 times more likely to experience gingivitis than their non-pregnant counterparts. This marked difference highlights the substantial impact that pregnancy-related physiological changes have on oral health.
Causes and Physiological Mechanisms
The primary cause of pregnancy gingivitis is the dramatic hormonal fluctuations that occur during pregnancy, particularly the significant increase in progesterone and estrogen levels. These hormonal changes directly affect the body’s response to oral bacteria and plaque, creating conditions that favor gingival inflammation.
Hormonal Influences on Gum Tissue
Progesterone plays a particularly important role in the development of pregnancy gingivitis. Elevated progesterone levels trigger an exaggerated inflammatory response to plaque bacteria that would normally be present in the mouth. This heightened reactivity makes the gum tissues more sensitive to irritants, resulting in increased inflammation even with relatively small amounts of plaque.
Estrogen further compounds these effects by altering the oral environment. Together with progesterone, these hormones can change the pH balance of the mouth and temporarily raise blood sugar levels, creating more favorable conditions for oral pathogens to thrive and proliferate. These hormonal changes essentially lower the threshold at which gingival tissues will become inflamed in response to bacterial biofilm.
Microbial Factors
The gram-negative bacterium Fusobacterium nucleatum, commonly found in gingivitis, has been identified as particularly problematic during pregnancy. This bacterium has been frequently isolated from amniotic fluid cultures of pregnant women experiencing premature labor, suggesting a potential connection between oral bacteria associated with gingivitis and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
The hormonal environment during pregnancy may also selectively favor the growth of certain periodontal pathogens, making it easier for gingivitis-causing bacteria to accumulate in greater numbers. This shift in the oral microbiome, combined with increased tissue sensitivity, creates the perfect conditions for gingival inflammation to develop and persist throughout pregnancy.
Clinical Symptoms and Diagnosis
Pregnancy gingivitis presents with distinctive clinical signs and symptoms that pregnant women and healthcare providers should be vigilant about recognizing.
Common Signs and Symptoms
The most noticeable symptoms of pregnancy gingivitis include:
- Bleeding gums, particularly during brushing or flossing
- Redness and inflammation of the gingival tissues
- Swollen, puffy appearance of the gums
- Tenderness or soreness when pressure is applied to the gums
- In some cases, receding gums
- Occasionally, bad breath may be present
Bleeding during brushing or flossing is typically the earliest and most common sign of pregnancy gingivitis. Research reveals that most pregnant women (79%) have at least one site with bleeding on probing, with an average of 10% of total oral sites exhibiting bleeding. This bleeding occurs because the inflamed gingival tissues become more fragile and vascular, making them prone to bleeding with even gentle mechanical stimulation.
Distribution and Severity Patterns
Pregnancy gingivitis most commonly affects the anterior regions of the mouth, particularly the interdental papillae, which often appear enlarged and may bleed spontaneously in severe cases. The severity of pregnancy gingivitis varies considerably among women, with studies classifying approximately 15% of cases as moderate and 73% as severe. Interdental areas are particularly susceptible, with research showing that 66.7% of interdental sites may demonstrate bleeding when stimulated with interdental brushes.
Dental professionals diagnose pregnancy gingivitis through clinical examination, measuring parameters such as bleeding on probing, probing depth, and gingival inflammation. The condition is differentiated from regular gingivitis primarily by its timing (occurring during pregnancy), its often increased severity, and its tendency to resolve after childbirth.
Risk Factors and Associations
Several factors influence a pregnant woman’s likelihood of developing gingivitis during pregnancy, with some increasing the risk significantly.
Demographic and Behavioral Risk Factors
Poor oral hygiene stands out as the most significant risk factor for developing pregnancy gingivitis. Research shows that pregnant women with poor oral hygiene practices are approximately 20 times more likely to develop gingivitis compared to those with good oral hygiene habits. Specifically, not using oral hygiene aids such as dental floss or interdental brushes increases the risk substantially (ORa = 6.76).
Inadequate dental care is another major risk factor. Pregnant women who do not attend regular dental check-ups have a significantly higher risk of developing gingivitis (ORa = 3.74). This is particularly concerning given that studies report as many as 88% of pregnant women in some populations have never received any form of professional oral health care.
Other factors that have been associated with increased risk include:
- Gravidity and parity (the number of pregnancies and births), with multiparous women showing higher rates of gingivitis
- Professional activity status, with employed women showing higher odds for gingivitis in some studies (OR = 6.75)
- Educational level, with varying associations across different populations
Protective Factors
Some protective factors have also been identified. Dietary habits, particularly the consumption of fruits and vegetables, appear to have a protective effect. Women who consume more than five portions of fruits and vegetables daily have significantly lower odds of developing gingivitis during pregnancy (OR = 0.15). This suggests that nutritional factors may play an important role in maintaining natural healthy teeth during pregnancy.
Interestingly, a higher body mass index (BMI) has been associated with lower odds of gingivitis in some studies (OR = 0.76), although this finding requires further investigation to understand the underlying mechanisms.
Impact on Pregnancy Outcomes
One of the most significant concerns regarding pregnancy gingivitis is its potential impact on pregnancy outcomes and fetal development.
Association with Preterm Birth
Research evidence suggests a relationship between untreated gingivitis during pregnancy and an increased risk of preterm birth. A meta-analysis of clinical trials found that treatment of gingivitis during pregnancy was associated with a significantly decreased risk of preterm birth (OR = 0.44, 95% CI [0.20–0.98], P = 0.045). This represents a 56% reduction in preterm birth risk when gingivitis is properly treated, highlighting the importance of addressing this condition during pregnancy.
Effects on Birth Weight
The same meta-analysis demonstrated that treatment of gingivitis during pregnancy was associated with higher birth weight in newborns (weighted mean difference = 105.36 g, 95% CI [36.72–174.01], P = 0.003). This suggests that maternal oral health has a meaningful impact on fetal development and growth.
Mechanisms of Adverse Outcomes
The relationship between oral health and pregnancy outcomes likely involves several pathways. The gram-negative bacterium Fusobacterium nucleatum, commonly found in gingivitis, has been isolated from amniotic fluid cultures obtained from pregnant women with premature labor and intact placental membranes. This suggests that oral bacteria may potentially translocate to the amniotic environment.
Additionally, gingivitis involves systemic dissemination of inflammatory mediators such as IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α. These inflammatory cytokines are known to play a role in the initiation of labor, and their elevated presence due to gingivitis may potentially contribute to adverse pregnancy outcomes. The evidence increasingly suggests that controlling gingival inflammation during pregnancy may have benefits beyond oral health, potentially improving pregnancy outcomes.
Safe Treatment Options During Pregnancy
Addressing pregnancy gingivitis appropriately is crucial, and fortunately, several safe and effective treatment options are available for pregnant women.
Professional Dental Care
Professional dental care is both safe and recommended throughout pregnancy. Major health organizations, including the American Dental Association and the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, encourage pregnant women to maintain regular dental visits. In the UK, NHS dental care is provided free of charge during pregnancy and for the first year after childbirth, highlighting the importance placed on maternal oral health.
Professional interventions that are considered safe during pregnancy include:
- Routine dental cleanings and examinations
- Non-surgical periodontal therapy, including scaling and root surface instrumentation, particularly during the second trimester
- Necessary dental extractions
- Dental X-rays with appropriate shielding
- Local anesthesia when required for treatment
Dentists may recommend more frequent cleanings during pregnancy, particularly during the second trimester or early third trimester, to help combat the effects of increased hormonal levels. While dental cleanings are generally safe throughout pregnancy, many dental professionals suggest scheduling elective dental procedures during the second trimester when possible.
Medications and Safety Considerations
When medication is necessary for dental treatment during pregnancy, certain precautions should be taken. Common painkillers and systemic antibiotics are generally considered safe, but tetracyclines and metronidazole should be avoided during pregnancy. Any medication should be prescribed to pregnant women only after consultation with their obstetrician.
For pregnancy-related gingival enlargements (pregnancy epulis), surgical excision is typically delayed until after delivery, with supportive plaque removal measures implemented during pregnancy instead. Similarly, extensive traumatic interventions such as periodontal surgery should be avoided during pregnancy when possible, particularly during the first trimester.
Prevention and Home Care Strategies
Effective prevention and management of pregnancy gingivitis largely depend on rigorous oral hygiene practices and healthy lifestyle choices. Using the right dental health products is essential for maintaining optimal oral health during pregnancy.
Optimal Oral Hygiene Practices
For pregnant women, the following oral hygiene practices are recommended:
- Brush teeth carefully twice daily for two minutes using fluoride toothpaste
- Use a soft-bristled, small-headed toothbrush to minimize gum irritation
- Floss at least once daily to remove interdental plaque
- Consider using additional interdental cleaning aids as recommended by dental professionals
- After episodes of morning sickness, rinse the mouth with plain water to neutralize acids before brushing
These basic practices can significantly reduce plaque buildup and help prevent or minimize gingival inflammation. The importance of proper technique cannot be overstated, as mechanical plaque removal remains the cornerstone of gingivitis prevention and treatment.
Dietary and Lifestyle Recommendations
Several dietary and lifestyle factors can influence gingival health during pregnancy:
- Limit consumption of sugary foods and drinks, and try to confine them to mealtimes rather than snacking throughout the day
- Choose healthier snacks such as fresh vegetables, fruits, or plain yogurt between meals
- Increase consumption of fruits and vegetables, aiming for more than five portions daily
- Avoid alcohol-containing mouthwashes, which may irritate sensitive gum tissues
- Stop smoking, as it can significantly worsen gum disease
- Maintain regular dental check-ups throughout pregnancy
Nutritional factors appear particularly important, with research showing that higher fruit and vegetable consumption is associated with significantly lower odds of developing gingivitis during pregnancy. This suggests that a nutrient-rich diet may help support gingival health through various mechanisms, including improved immune function and reduced inflammation.
Preventing Complications and Long-term Oral Health
Maintaining good oral hygiene during pregnancy not only helps prevent gingivitis but also reduces the risk of other dental issues like tooth decay. Untreated gingivitis can potentially progress to more severe periodontal disease if neglected, which may have long-lasting consequences beyond pregnancy.
Conclusion
Pregnancy gingivitis affects the majority of pregnant women, with prevalence rates consistently ranging from 60-75% across diverse populations. The condition is primarily driven by hormonal changes during pregnancy that heighten the gingival response to bacterial plaque. While generally temporary and resolving after childbirth, untreated gingivitis during pregnancy has been associated with concerning outcomes, including increased risk of preterm birth and lower birth weight.
The good news is that pregnancy gingivitis is both preventable and treatable. Effective plaque control through proper brushing and flossing, combined with regular professional dental care, forms the foundation of prevention and management. Dental treatments including cleanings, scaling, and necessary restorative procedures are considered safe during pregnancy, particularly during the second trimester. Nutritional factors, especially adequate consumption of fruits and vegetables, may provide additional protective benefits.
Healthcare providers should work together to increase awareness about pregnancy gingivitis and its potential implications. Obstetricians, midwives, and primary care providers can play a crucial role in referring pregnant women for dental evaluation, while dental professionals can provide tailored oral hygiene instruction and appropriate treatment. With proper attention to oral health, pregnant women can minimize gingival inflammation and potentially improve both maternal and fetal outcomes.
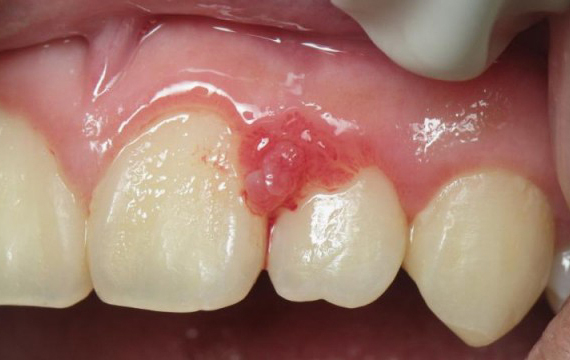
Gingivitis and Hormonal Changes: Why Women Are More Susceptible
Women face a unique set of oral health challenges due to hormonal fluctuations throughout their lives. Emerging research reveals that women experience a heightened risk of **gingivitis **and periodontal disease during specific hormonal milestones from puberty through menopause. This relationship between hormonal changes and oral health represents a significant but often overlooked aspect of women’s healthcare. The following report examines the biological mechanisms behind increased gingival sensitivity during hormonal transitions, identifies high-risk periods, and outlines preventive strategies for optimal oral health maintenance.
The Hormonal-Oral Health Connection Women’s susceptibility to oral health problems stems from the unique hormonal changes they experience throughout their lives. These hormonal fluctuations, particularly in estrogen and progesterone levels, significantly impact the oral environment in multiple ways. Hormones affect not only the blood supply to gum tissue but also alter how the body responds to toxins produced by plaque buildup. This hormonal influence creates periods of increased vulnerability to gingivitis and periodontal disease during specific life stages.
The biological mechanism behind this relationship is multifaceted. Estrogen primarily affects blood vessels and the cytodifferentiation of stratified squamous epithelium, while also influencing the synthesis and maintenance of fibrous collagen. Estrogen receptors in osteoblast-like cells provide a direct pathway for hormonal action on bone, while similar receptors in periodontal ligament fibroblasts enable hormones to directly impact periodontal tissues. Meanwhile, progesterone stimulates the production of inflammatory mediators, potentially exacerbating the inflammatory response to bacterial presence.
Additionally, certain microorganisms found in the human mouth can synthesize enzymes needed for steroid hormone metabolism, creating a complex interplay between oral bacteria and hormonal fluctuations. This bacterial adaptation to the hormonal environment contributes to the increased gingival inflammation observed during periods of hormonal change in women.
Manifestations of Hormone-Induced Gingival Changes
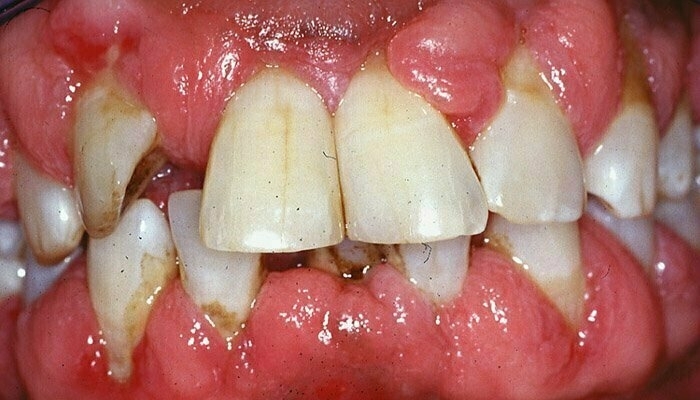
Hormone-influenced gingivitis typically manifests as red, swollen, tender gums that bleed more easily during brushing and flossing. The increased blood flow to gum tissues due to hormonal fluctuations can change how gum tissue reacts to plaque irritants, making the gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation. In severe cases, women may experience significant gingival enlargement, increased bleeding, and even the development of pyogenic granulomas—non-cancerous growths on the gum tissue that can be painful and bleed easily.
Vulnerable Periods Throughout a Woman’s Life Puberty and Adolescence The onset of puberty marks the first significant period of hormonal flux affecting oral health. During adolescence, the surge in production of estrogen and progesterone increases blood flow to the gums and alters how gum tissue responds to plaque irritants. Adolescent gingivitis typically begins around the age of 8-13, coinciding with the onset of puberty. This condition presents as swollen, red, tender gums that may bleed during brushing and flossing.
The hormonal changes during this period not only affect physical oral health but can also impact psychological aspects. As adolescence may affect girls' self-esteem and body image, maintaining healthy oral health becomes important for supporting overall confidence. Furthermore, dietary habits often change during adolescence, and orthodontic treatments frequently begin during this time, making good oral hygiene particularly crucial for preventing decay and gum inflammation.
The Menstrual Cycle Monthly hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can trigger transient changes in gingival health. Due to the hormonal shifts (particularly increased progesterone) during the menstrual cycle, some women experience oral changes including bright red swollen gums, swollen salivary glands, development of canker sores, or bleeding gums. This condition, sometimes called “menstruation gingivitis,” typically occurs a day or two before the start of menstruation and usually resolves shortly after the period begins.
Research has shown that women with pre-existing gingivitis often experience a worsening of their condition during menstruation, while those without clinical gingivitis show no increase in gingival inflammation. Studies have demonstrated that TNF-α shows significant fluctuation during the menstrual cycle, with surges just before ovulation and pre menstruation, suggesting it may serve as a mediator through which gingival inflammation is modulated. Birth Control Pills
Women who use hormonal contraceptives containing progesterone may experience amplified gingival responses to plaque. When taking certain birth control pills that contain progesterone, women may experience inflamed gum tissues due to the body’s exaggerated reaction to the toxins produced from plaque. This increased sensitivity makes proper oral hygiene even more important for women on hormonal contraceptives.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy represents a period of particularly dramatic hormonal fluctuations that significantly impact oral health. Approximately 40% of pregnant women develop gingivitis at some point during their pregnancy, with symptoms typically appearing between the second and eighth month and peaking during the third trimester. The surge in progesterone during pregnancy can encourage the growth of bacteria in plaque around the teeth and gums, increasing gum sensitivity and leading to inflammation and infection.
Pregnancy gingivitis manifests as swollen, red, and tender gums that may bleed during brushing and flossing. In more severe cases, pregnancy gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which involves infection and inflammation of the connective tissues around the teeth, potentially leading to permanent damage.
Of particular concern is the established link between periodontal disease during pregnancy and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Research has shown that pregnant women with periodontitis may be up to seven times more likely to have a baby born with low birth weight or prematurely (before 37 weeks). These complications can lead to various health challenges for the newborn, including an increased risk of learning difficulties as children.
Menopause
The decline in ovarian steroids during menopause promotes important changes in connective tissue throughout the body, including oral tissues. Women in perimenopause and menopause are more likely to develop bleeding gums and other symptoms of gum disease primarily due to inflammation. As estrogen levels fluctuate and eventually decline during perimenopause, some of the anti-inflammatory protection provided by estrogen disappears.
Studies show that estrogen can suppress inflammation in certain cells of the body, and its absence during menopause can lead to increased inflammatory responses in the gums. Furthermore, decreased estrogen levels can lead to burning mouth syndrome, dry mouth, and changes in taste perception. Menopausal women are also more prone to gum disease and receding gum tissue due to these hormonal changes.
The Bidirectional Relationship Between Hormones and Oral Health
Interestingly, the relationship between hormonal imbalance and gum disease works bidirectionally. Not only do hormonal fluctuations increase susceptibility to gum disease, but poor oral hygiene leading to gingivitis can potentially exacerbate hormonal imbalance. When poor oral hygiene leads to bleeding gums, it can activate and elevate the inflammatory response throughout the body, potentially contributing to systemic inflammation that may influence hormonal balance.
Research increasingly demonstrates that periodontal disease affects the entire body, not just the mouth. Bleeding gums may signal other inflammatory issues beyond hormonal imbalance, highlighting the importance of oral health as a component of overall systemic health.
Prevention and Management Strategies Consistent Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining diligent oral hygiene becomes especially important during hormonal transitions. Women should brush at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush to minimize irritation to sensitive gums. Daily flossing is crucial for removing trapped food particles and bacteria between teeth that brushing alone cannot reach. For those experiencing heightened sensitivity, using an antimicrobial mouthwash without alcohol can help control bacterial growth. ** Regular Dental Visits**
Professional dental care plays a vital role in managing hormone-related gingival changes. Women should schedule regular dental checkups and cleanings, with increased frequency during high-risk periods like pregnancy. Professional cleanings can remove plaque and tartar buildup that contributes to gingival inflammation, helping to control the cycle of inflammation and infection. Dentists can also monitor for early signs of hormone-related oral changes and intervene before conditions worsen.
Diet and Lifestyle Considerations
Nutritional choices significantly impact oral health during hormonal fluctuations. A balanced diet low in sugary foods and beverages helps reduce bacterial growth that contributes to plaque formation. Increasing consumption of fruits and vegetables provides essential nutrients that support gum health and immune function. Staying well-hydrated helps maintain adequate saliva production, which serves as a natural defense against oral bacteria.
Special Considerations During Pregnancy Pregnant women require particular attention to their oral health due to both increased susceptibility to gingivitis and potential impacts on pregnancy outcomes. Women planning pregnancy should consider a pre-conception dental checkup to address any existing oral health issues. During pregnancy, scheduling a dental cleaning in the second or third trimester allows for assessment of overall oral health and management of any developing issues.
For active swelling and bleeding gums during pregnancy, treatment typically involves a series of preventative or deep cleanings to physically remove bacteria below the gum lines, helping to control inflammation and infection. This intervention is particularly important given the established links between untreated gum infections and increased risk of preeclampsia and preterm birth.
Conclusion Women’s hormonal fluctuations throughout life create periods of increased vulnerability to gingivitis and periodontal disease. From puberty through menopause, the complex interplay between hormones—particularly estrogen and progesterone—and oral tissues significantly impacts gum health. Understanding these connections enables women to implement targeted prevention strategies during high-risk periods.
The relationship between hormonal changes and oral health represents an important yet often overlooked aspect of women’s healthcare. Greater awareness among both women and healthcare providers about these connections can lead to improved preventive care and better oral health outcomes. By recognizing the signs of hormone-influenced gingivitis and implementing appropriate oral hygiene practices, dietary choices, and professional dental care, women can maintain optimal oral health throughout the various hormonal transitions of their lives.
Future research opportunities include exploring specific preventive approaches targeted to each hormonal stage and investigating potential treatments that address both hormonal balance and oral inflammation simultaneously. As our understanding of the relationship between hormones and oral health continues to evolve, so too will our ability to develop more effective strategies for prevention and management.
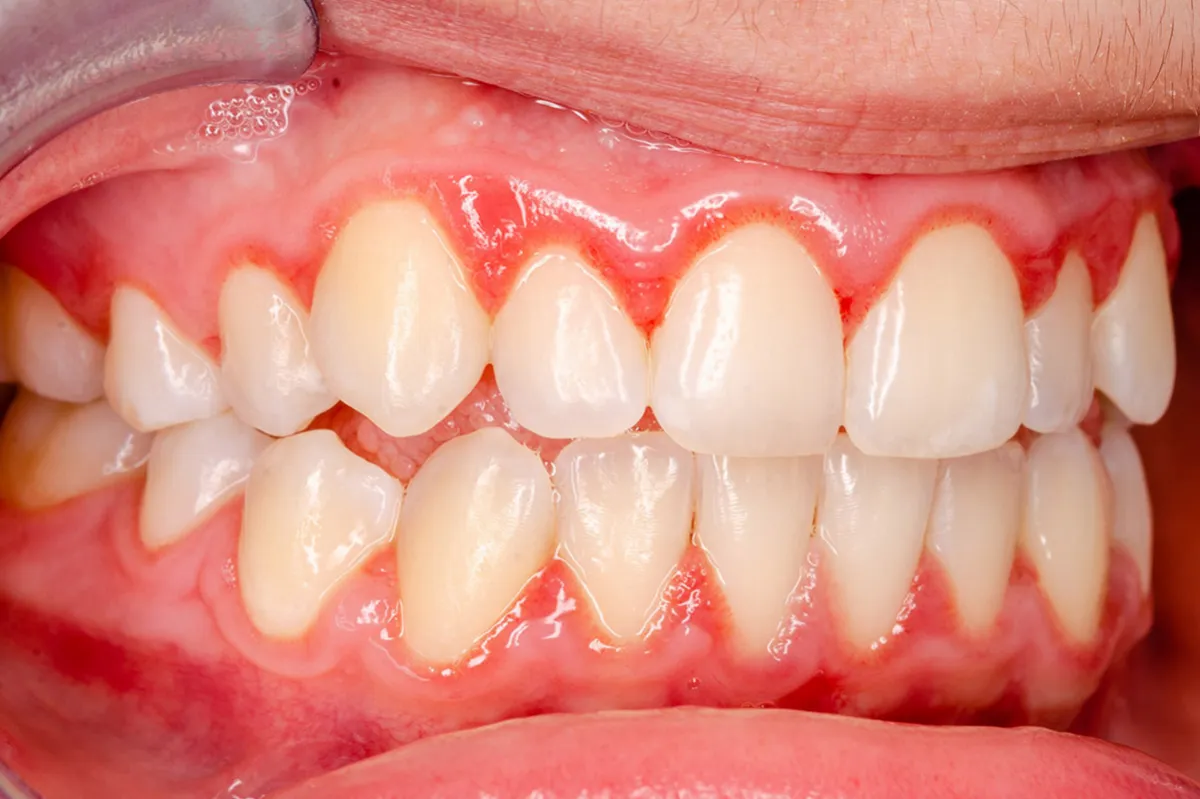

Gingivitis vs Periodontitis: Key Differences Explained
Just published a comprehensive guide comparing gingivitis vs. periodontitis. This article breaks down the key differences, warning signs, and treatment options for both conditions. I’ve included natural remedies, prevention strategies, and expert insights to help you protect your gums and overall health.
Check it out if you’ve ever noticed bleeding when brushing or are concerned about gum disease. *Gingivitis vs. Periodontitis*.
#dentalhealth #oralcare #gumdisease #gingivitis #periodontitis
Conquering Dry Mouth: Simple Solutions for Daily Relief
Dry mouth affects millions, causing discomfort and potentially serious oral health issues. Beyond the annoying feeling of thirst, it can lead to increased cavities, gum disease, and difficulty speaking or swallowing. The good news? Several effective strategies can help:
Stay hydrated by sipping water throughout the day Try sugar-free lozenges or gum to stimulate saliva production Use a humidifier at night to keep air moist Avoid alcohol-containing mouthwashes which can worsen dryness Consider OTC saliva substitutes for temporary relief
If medications are causing your dry mouth, speak with your doctor about alternatives. For persistent symptoms, a dental professional can recommend specialized products and treatments. Don’t ignore dry mouth—these simple interventions can significantly improve your comfort and protect your oral health. How to Manage Dry Mouth
#OralHealth #DryMouthRelief #DentalTips

Teeth Whitening with Strawberries: The Science Reveals Why This Popular DIY Remedy Doesn't Work
Discover the truth about teeth whitening with strawberries: science reveals why this popular DIY remedy doesn’t work and may harm enamel. Learn safer alternatives for a brighter smile.
Read More on teeth whitening with strawberries

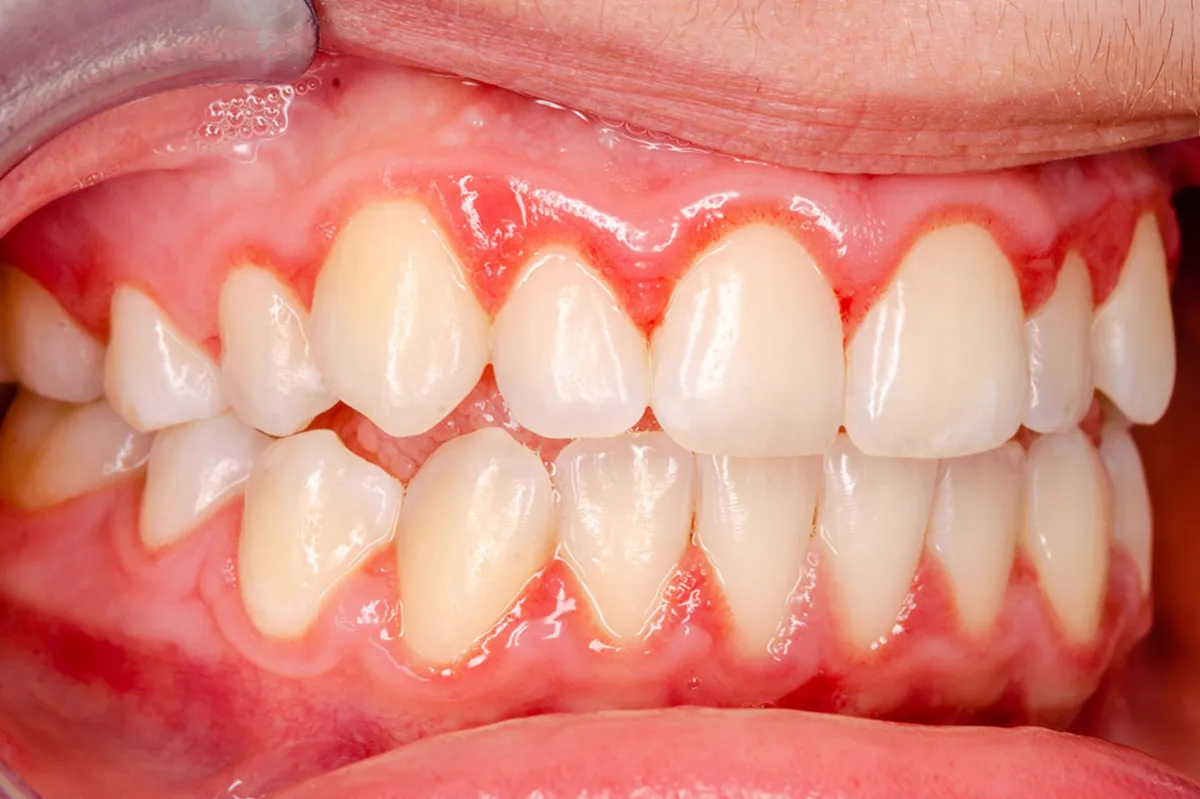
Best Toothpaste for Gingivitis: Expert Guide to Gum Health
Find the Best Toothpastes for Gingivitis backed by dental experts.Discover dentist recommended brands and treatments for healthier gums. Gingival Toothpaste Best Toothpaste for Gingivitis
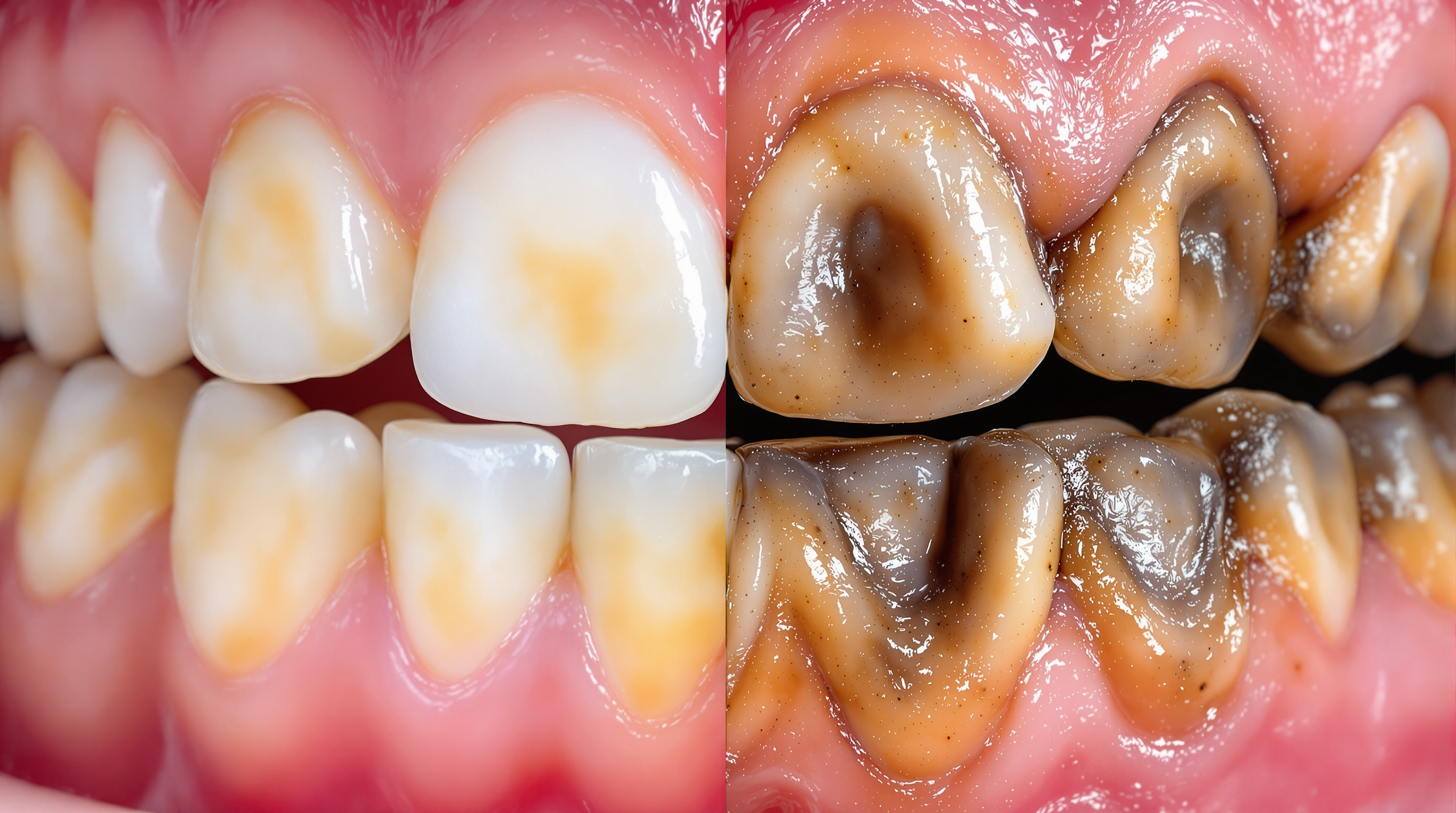
Rotten Teeth: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
Discover the causes of rotten teeth, early warning signs, and treatment options from fluoride therapy to root canals. Learn prevention strategies and why 30,000 children require tooth extractions yearly. Rotten Teeth
Best Toothbrush for Sensitive Gums: Expert Guide
Discover the best toothbrush for sensitive gums that provides gentle yet effective cleaning. Learn how to reduce discomfort and protect your gum health with our expert recommendations. Best Toothbrush for Sensitive Gums

JFK Files Released: Key Findings, Conspiracy Theories, and the Kennedy Legacy
The latest JFK files released reveal fresh insights into the JFK assassination, Lee Harvey Oswald, and the enduring Kennedy legacy. Read on for facts, controversies, and how to access these documents. The latest JFK files released
#JFKFiles #KennedyLegacy #JFKAssassination #HistoricalTransparency #CIA #ConspiracyTheories

Sean ‘Diddy’ Combs: Legal Battles, Music Drama & Cultural Impact in 2025
Sean ‘Diddy’ Combs faces federal charges of sex trafficking and racketeering amid civil lawsuits, custody battles, leaked prison calls, and explosive music and family controversies that fuel a media storm in 2025. Sean ‘Diddy’ Comb
#Diddy #KanyeWest #KimKardashian #NorthWest #BadBoyRecords #Yeezy #FederalTrial #CivilLawsuits #CelebrityNews #MusicIndustry

John Cena’s Explosive Rant on Monday Night Raw: A Heel Turn That Shook WWE
John Cena’s shocking rant on Monday Night Raw in Brussels, Belgium, marked a historic heel turn, setting the stage for WrestleMania 41 and his retirement. Here’s an in-depth analysis of the event. John Cena’s Explosive Rant on Monday Night Raw
#JohnCena #WWE #MondayNightRaw #HeelTurn #FanRant #CodyRhodes #WrestleMania41 #Retirement #WrestlingNews

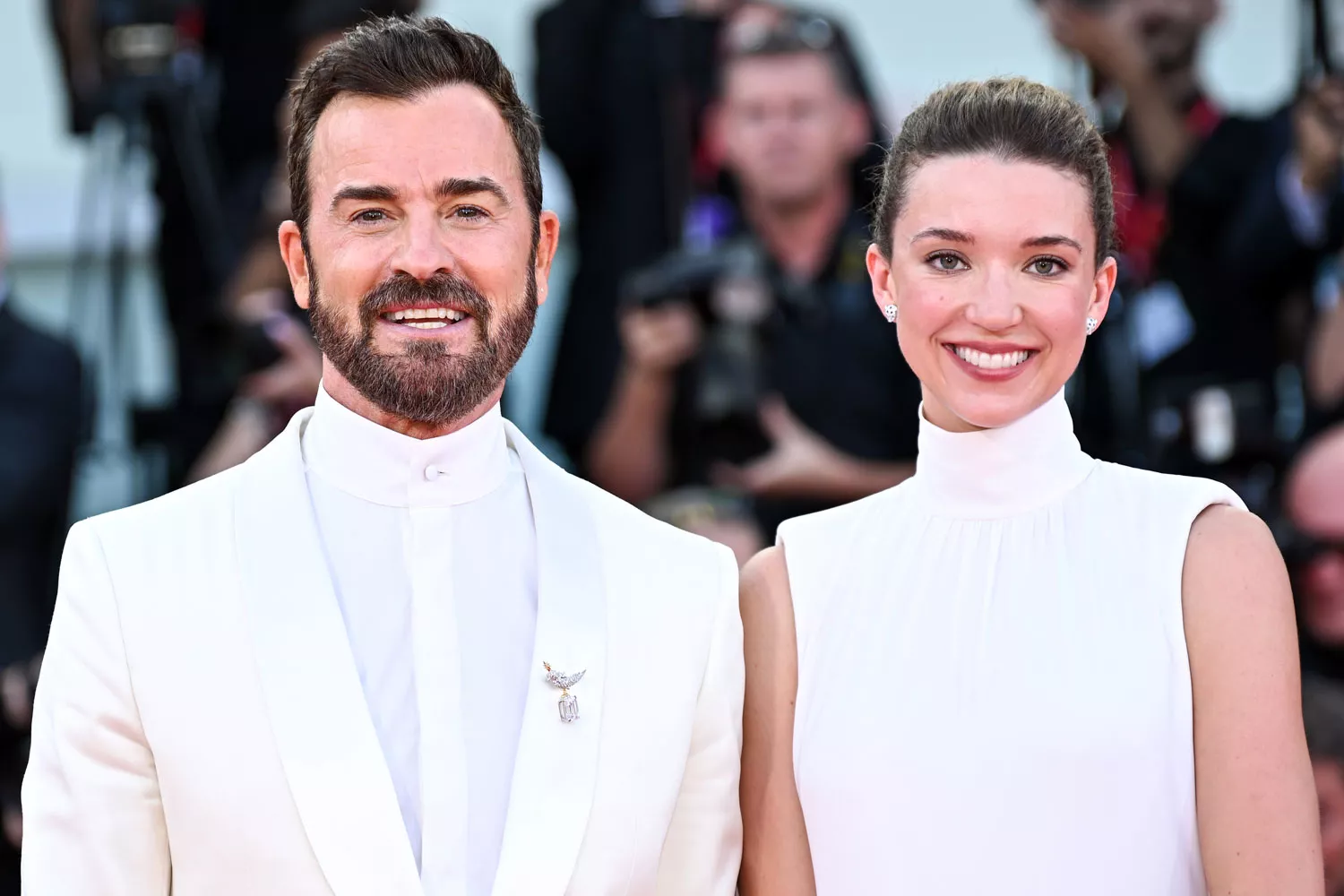
Inside Justin Theroux and Nicole Brydon Bloom's Star-Studded Destination Wedding in Mexico
Justin Theroux and Nicole Brydon Bloom’s star-studded destination wedding at Hotel Esencia in Xpu Há, Mexico dazzled with stilt-walkers, a mariachi band, swimming mermaids, and top celebrity guests. **Justin Theroux and Nicole Brydon Bloom’s Wedding **
#JustinTheroux #NicoleBrydonBloom #DestinationWedding #CelebrityWeddings #WeddingInspiration

BYD Shares Surge: How 5-Minute Charging Technology is Transforming the EV Market
BYD shares surge after unveiling 5-minute charging tech powering new Han L sedan and Tang L SUV. With 4,000 charging stations planned, this breakthrough is redefining the EV market vs. Tesla. Read!!!! BYD shares surge
#BYD #EVs #FastCharging #ElectricVehicles #Tesla #StockMarket #Innovation #China

: Impact of Phone Claims, In-Person Filing, and Accessibility on Vulnerable Populations
Latest Social Security changes in 2025 reshape phone claims, in-person filing, and digital access. Understand effects on elderly, disabled, and limited mobility groups amid rising hardship and modern trends. Social Security Changes in 2025

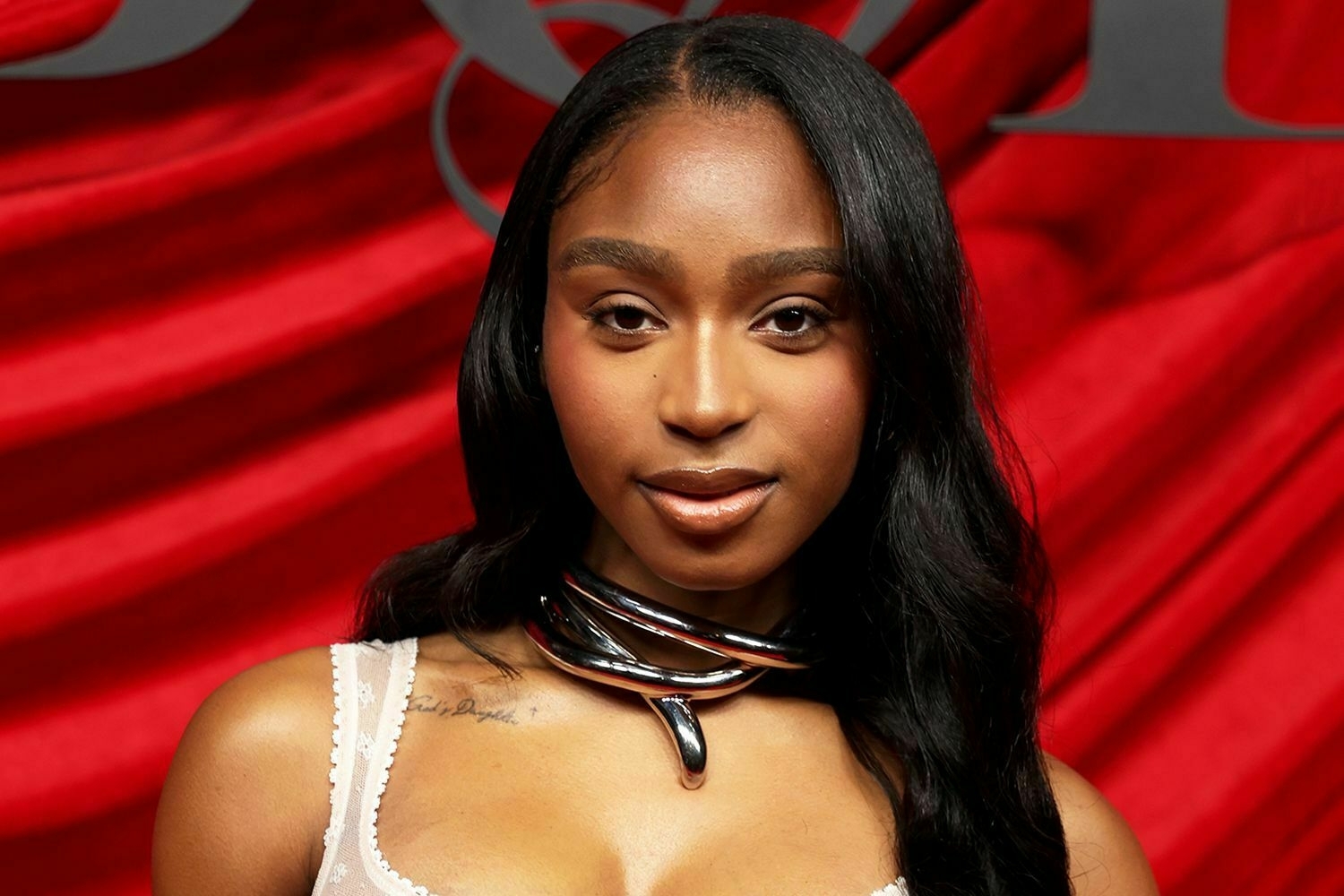
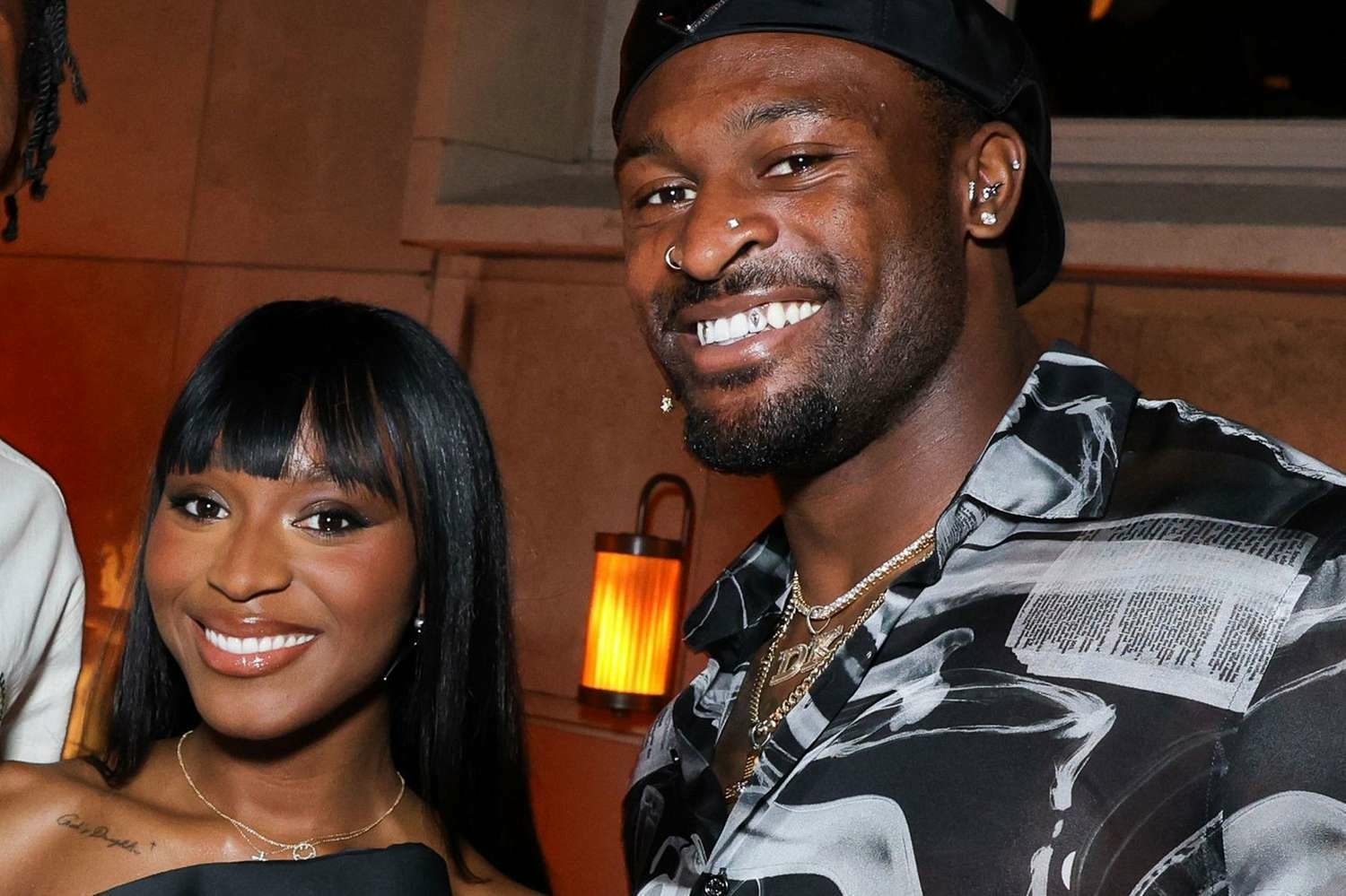
Normani and DK Metcalf's Engagement: A Love Story of Music and Sports
In a headline-making marriage of music and sports, excitement is building around the reported engagement of Normani and DK Metcalf. This detailed article provides an in-depth analysis of their personal journeys, the special moments that led to their union, and the cultural impact of their romance. Covering everything from career highlights to behind-the-scenes details of the proposal, the following sections offer a comprehensive look at this influential couple, supported by data, credible external sources, and expert reflections on modern celebrity relationships. Read more on Normani engagement to DK Metcalf


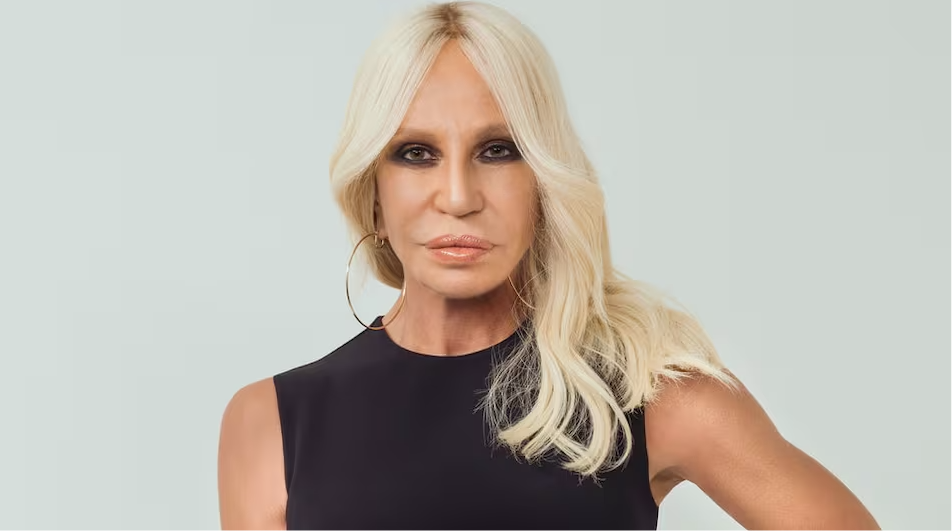
Donatella Versace Steps Down: The Legacy of Versace, Gianni Versace, and Miu Miu's Influence
In a transformational moment for the luxury fashion industry, Donatella Versace has recently stepped down as the creative director of Versace after a remarkable 28‑year tenure. This change marks not only the end of an era but also the beginning of a new chapter—one that honours the incomparable legacy of her late brother, Gianni Versace, while embracing a fresh vision inspired by modern influences from brands like Miu Miu.
Today’s article provides an in‑depth exploration of Donatella Versace’s storied career, the evolution of the Versace brand, the foundational influence of Gianni Versace, and the exciting implications of Miu Miu’s aesthetic on the future of one of fashion’s most celebrated labels. Read more on Donatella Versace
#Versace #DonatellaVersace #GianniVersace #MiuMiu #LuxuryFashion #FashionLegacy #ModernTrends


Dawn Robinson: The Iconic Voice Behind En Vogue and Her Inspiring Journey Beyond the Spotlight
In a heartfelt revelation on her YouTube channel, Dawn Robinson, a founding member of the iconic ’90s group En Vogue, shared that she’s been living in her car for nearly three years. Known for hits like “My Lovin’” and “Hold On,” Robinson opened up about her struggles despite her past success.
She mentioned that she initially hesitated to reveal her situation due to fears of judgment, but ultimately decided to share her truth. “We’re all judged. Life is life,” Robinson stated, emphasizing the universality of life’s challenges.
Robinson recounted that in 2020 she was living with her parents in Las Vegas, which was great until circumstances changed. After spending a month living in her car, she accepted an offer from her co-manager to stay with him in Los Angeles.
Her candidness sheds light on the often-hidden struggles many face, reminding us that life’s difficulties can affect anyone, regardless of their past achievements. Read on

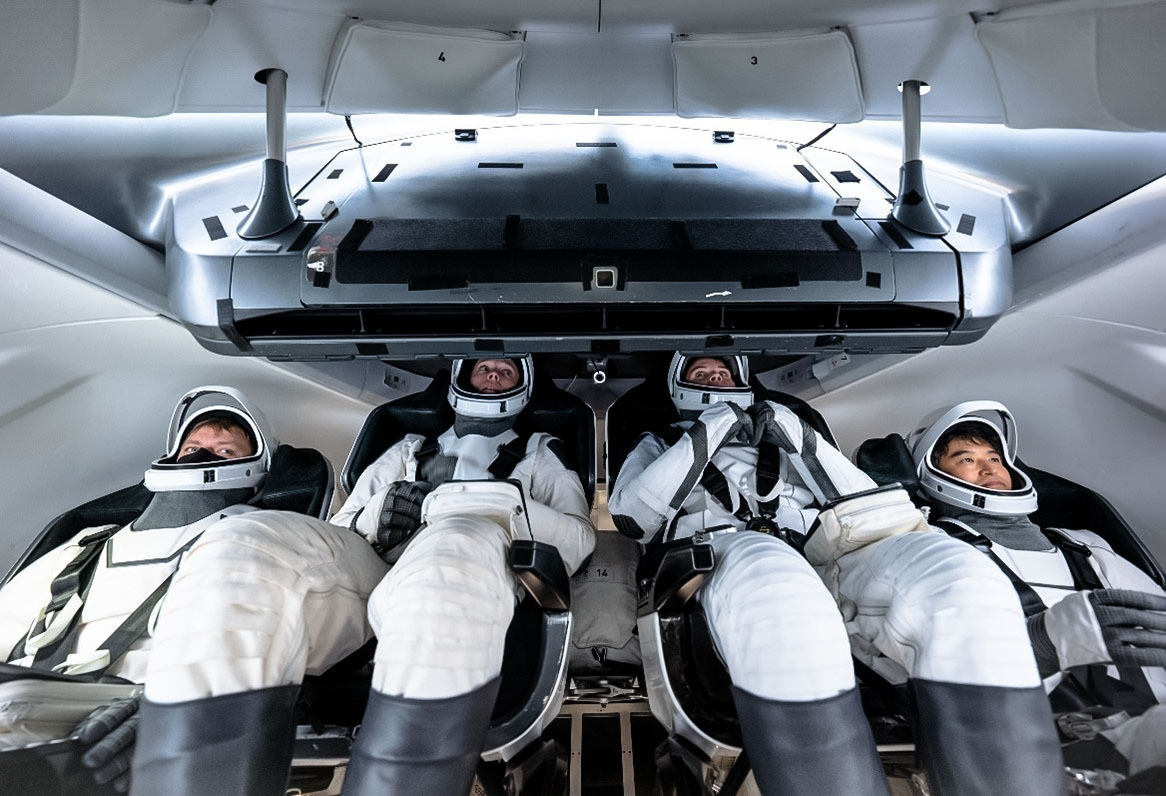
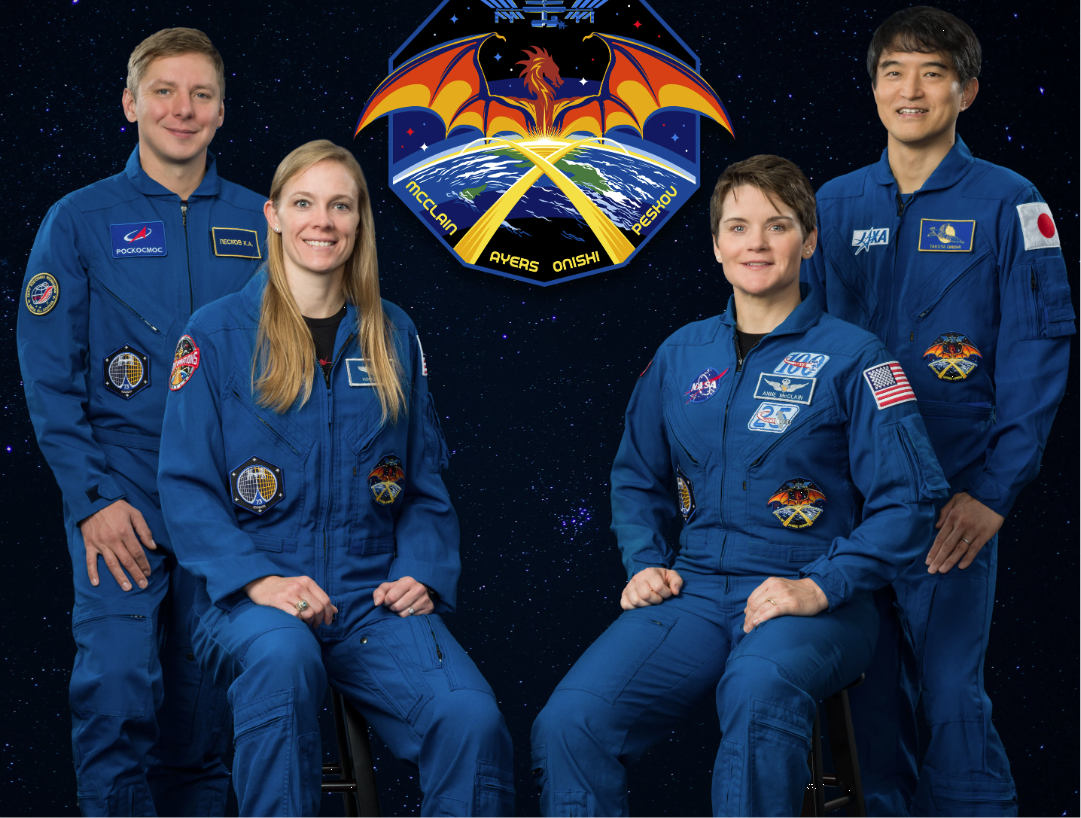
NASA SpaceX Crew-10 Launch: Everything You Need to Know About This Historic Mission
The NASA SpaceX Crew 10 launch is set to redefine space travel with 4 astronauts bound for the ISS. Get live launch details, expert insights & mission updates – must-read info for space enthusiasts. NASA SpaceX Crew 10 launch
SpaceX launch scrubbed: Hydraulic issue delays Crew-10 mission to ISS. NASA & SpaceX aim for next launch window Thursday at 7:25 p.m. Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth shared a heartfelt message with the crew: “We are praying for you. Wish you Godspeed.” 🚀 #SpaceX #Crew10 #LaunchDelay


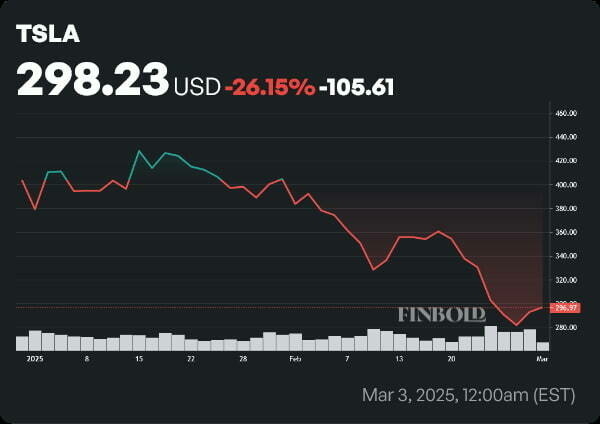
Tesla Stock in 2025: Trends, Insights and Future Predictions
Tesla stock in 2025 shows volatility amid fierce competition and declining prices. Real-time data, expert forecasts, and actionable insights reveal TSLA trends, Elon Musk net worth impacts, and future market dynamics. Tesla Stock Crash
#TeslaStock #TSLA #ElonMusk #SpaceX #EV #StockMarket #Innovation #TechTrends